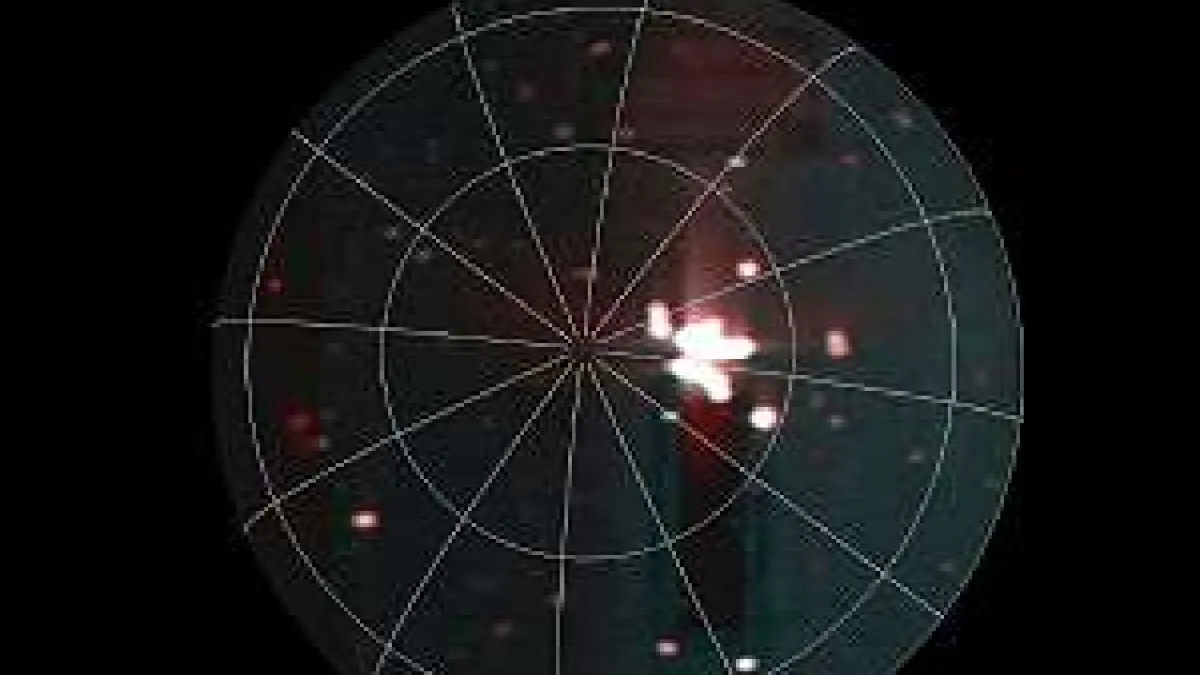
NASA’s Juno spacecraft, which has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, has made an extraordinary discovery that continues to captivate scientists and astronomers alike: record-breaking volcanic activity on Jupiter’s moon, Io. This discovery marks a significant milestone in space exploration, revealing new insights into the most geologically active body in the Solar System. Io, one of Jupiter’s 79 moons, has long been known for its intense volcanic activity, but the data collected by Juno has pushed our understanding of this dynamic moon to new heights. In this article, we’ll dive into the findings of NASA’s Juno mission, what makes Io’s volcanic activity so unique, and the implications of this discovery for future space exploration.
NASA’s Juno Mission: A Game Changer in the Study of Io
The Juno mission, primarily designed to study Jupiter, has provided unprecedented insights into the gas giant’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons. However, one of its most fascinating discoveries has been its ability to observe Io’s volcanic activity in greater detail than ever before. Through Juno’s flybys of Jupiter’s moon system, scientists have been able to observe Io’s surface in real-time, capturing data on volcanic eruptions and the immense energy being released from the moon’s interior.
The spacecraft’s unique instruments, including the Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) and the JunoCam, have allowed scientists to observe Io’s volcanoes in a way that was previously impossible. Juno’s ability to capture infrared images has provided detailed information on the heat emitted from volcanic eruptions, revealing the full scale of Io’s geologic activity. This breakthrough is a game-changer in planetary science, as it allows for a deeper understanding of volcanic processes not only on Io but also on other moons and planets in the Solar System.
Record-Breaking Volcanic Activity: What Makes Io So Unique?
Io is already well-known for its extreme volcanic activity, but the Juno mission has revealed that this volcanic activity is even more intense and widespread than scientists had previously realized. The moon’s surface is dotted with hundreds of active volcanoes, many of which experience frequent eruptions. These eruptions are unlike anything seen on Earth, with lava temperatures reaching over 1,500 degrees Celsius (2,732 degrees Fahrenheit) and plumes of volcanic gas reaching hundreds of kilometers into space.
Io’s volcanic activity is largely driven by tidal heating, a process in which the moon’s interior is flexed and deformed by the immense gravitational pull of Jupiter and the other large moons, Europa and Ganymede. This constant flexing generates friction inside the moon, which in turn produces enormous amounts of heat. This heat causes the interior of Io to remain partially molten, fueling its active volcanoes. Unlike Earth, where tectonic plates play a major role in volcanic activity, Io’s volcanic eruptions are driven primarily by these tidal forces, making it one of the most geologically active bodies in the Solar System.
One of the most remarkable aspects of Io’s volcanic activity is its regularity. While Earth’s volcanoes tend to erupt sporadically, Io’s volcanoes are constantly in motion, with eruptions occurring at regular intervals. This constant volcanic activity plays a crucial role in reshaping Io’s surface, with new volcanic features emerging and old ones being destroyed at a rapid pace.
Juno’s Key Findings on Io’s Volcanic Activity
Juno’s flybys have provided an unprecedented view of Io’s volcanic landscape, allowing scientists to study the heat signatures of eruptions and the composition of the volcanic material being expelled. One of the most significant findings from Juno’s mission is the discovery of previously unknown volcanic hotspots on Io’s surface. These hotspots are areas of intense heat that are not always visible in visible light but can be detected using Juno’s infrared capabilities.
Through these infrared images, scientists have discovered new areas where lava is actively flowing, contributing to the creation of new volcanic features on the moon’s surface. The intensity of the heat being emitted from these hotspots suggests that Io’s volcanic activity may be more widespread than initially thought. Additionally, Juno’s data has revealed that the volcanoes on Io are capable of releasing vast amounts of sulfur dioxide and other gases into space, which contributes to the moon’s thick, sulfuric atmosphere.
The data collected by Juno has also allowed scientists to study the interaction between Io’s volcanic activity and its surrounding environment. The eruption plumes that shoot into space have been found to interact with Jupiter’s magnetic field, creating an intense radiation environment around Io. This interaction between the moon’s volcanoes and Jupiter’s magnetic field is a fascinating example of how celestial bodies can influence each other in complex ways, offering new avenues of study for future space missions.
The Implications of Juno’s Discovery for Space Exploration
NASA’s Juno mission has opened up exciting new possibilities for the study of volcanic activity on other celestial bodies. Io’s extreme volcanic behavior offers scientists a unique opportunity to study the processes that drive geological activity on moons and planets. Understanding how tidal heating generates such extreme volcanic eruptions on Io can provide valuable insights into similar phenomena that might occur on other moons, such as Europa or Enceladus, which are believed to harbor subsurface oceans beneath their icy crusts.
The discovery of such intense volcanic activity on Io also has implications for future space exploration missions. For one, understanding the behavior of Io’s volcanoes can help future spacecraft avoid hazardous conditions. The intense radiation around Io, generated by the interaction between the volcanic plumes and Jupiter’s magnetic field, could pose a significant challenge for spacecraft that venture too close to the moon. However, the information gathered by Juno could help mission planners design spacecraft that can safely navigate these dangerous environments.
Moreover, Io’s active volcanoes offer a unique opportunity for studying the processes of planetary formation and the evolution of planetary bodies. By studying how tidal forces drive such extreme volcanic activity, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the internal workings of moons and planets in our Solar System and beyond.
Could Io’s Volcanic Activity Be Harnessed for Energy?
While the idea of harnessing Io’s volcanic energy may seem far-fetched at the moment, the discovery of such massive energy production has sparked some interesting discussions about the potential for future energy sources beyond Earth. The enormous amount of heat generated by Io’s volcanic activity could theoretically be harnessed, provided the right technology and infrastructure were in place. However, given the extreme conditions on Io, including its distance from Earth and the challenges associated with its harsh environment, it’s likely that any such venture remains a distant possibility.
Instead, the true value of Io’s volcanic activity lies in its ability to help scientists learn more about the processes that drive geological activity on other worlds. These insights could have far-reaching applications for understanding the habitability of other moons and planets, as well as the potential for life to exist in extreme environments.
FAQs
1. What is the Juno mission, and how does it study Io? NASA’s Juno mission is a spacecraft that has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, studying the planet’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons. Juno uses instruments like the Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) and JunoCam to observe Io’s volcanic activity, capturing infrared data to reveal heat emissions from the volcanoes.
2. Why is Io so volcanically active? Io’s volcanic activity is primarily driven by tidal heating, which results from the gravitational interaction between Jupiter, Io, and other moons like Europa and Ganymede. This constant flexing of Io’s interior generates enormous amounts of heat, fueling the moon’s active volcanoes.
3. What has the Juno mission revealed about Io’s volcanic activity? Juno has discovered previously unknown volcanic hotspots on Io’s surface, revealing new areas of lava flow and volcanic eruptions. The spacecraft has also provided detailed infrared images of the heat emitted by the volcanoes, which has helped scientists understand the scale and intensity of Io’s volcanic activity.
4. How could Juno’s discoveries help future space exploration? The data collected by Juno can help future spacecraft avoid the hazardous conditions around Io, including its intense radiation environment. Additionally, studying Io’s volcanic activity provides valuable insights into geological processes that could be relevant for understanding other moons and planets in our Solar System.
5. Could Io’s volcanic activity be used for energy? While the idea of harnessing energy from Io’s volcanic activity is intriguing, it is not currently feasible due to the extreme conditions on the moon. However, the study of Io’s volcanoes provides valuable insights into planetary science and could influence future exploration of other celestial bodies.
Conclusion
NASA’s Juno mission has dramatically expanded our understanding of Io, revealing record-breaking volcanic activity that is unlike anything seen on Earth. The data collected by Juno has given scientists unprecedented insights into the mechanisms behind Io’s volcanic eruptions and the dynamic processes that shape the moon’s surface. As we continue to explore the far reaches of the Solar System, discoveries like these will continue to shape our understanding of other worlds and the forces at play within them. Whether it’s for scientific curiosity or the potential for future space exploration, the study of Io’s volcanic activity is an exciting frontier that promises to yield even more groundbreaking discoveries in the years to come.